- FOR US HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
- FOR PATIENTS & CAREGIVERS»
- Important Safety Information
- Medical Resources
In the treatment of cis-eligible MIBC
EVENT-FREE SURVIVAL (dual primary endpoint)1,3
REDUCTION IN RISK OF AN EVENT (progression, recurrence, death, or not undergoing RC)† with the NIAGARA Regimen‡ vs neoadjuvant gem-cis (HR=0.68 [95% CI, 0.56-0.82]; P<0.0001)
Median EFS was not reached with the NIAGARA Regimen‡ (95% CI, NR-NR) vs 46.1 months with neoadjuvant gem-cis (95% CI, 32.2-NR)
Median duration of follow-up: 42.3 months (range: 0.03-61.3).
EVENT-FREE SURVIVAL (dual primary endpoint)1,3
EFS BY PRESPECIFIED PATIENT SUBGROUP (exploratory analysis)1,3
|
|
|
|---|
SCROLL
The EFS prespecified patient subgroup analysis was not powered to show differences between or within individual subgroups and was not powered to determine statistical significance.3
*A perioperative regimen consists of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment.1
†Event-free survival was defined as the time from randomization to first recurrence of disease post-RC, time to first documented progression in patients who were precluded from RC, time of expected surgery in patients who refused RC or failure to undergo RC due to residual disease, or death due to any cause, whichever occurs first.3
‡The NIAGARA Regimen is defined as neoadjuvant IMFINZI + gem-cis followed by adjuvant IMFINZI as a single agent after RC.1
pCR RESULTS (dual primary endpoint): PRIMARY ANALYSIS AND EXPLORATORY REANALYSIS3
§The descriptive reanalysis of pCR included the results of 59 evaluable samples that were omitted from the primary analysis because the date of central assessment (which occurred after January 14, 2022), rather than the date of surgery (which occurred before January 14, 2022), was used as the data cutoff date.
NCCN
CATEGORY 1,
PREFERRED
Neoadjuvant durvalumab (IMFINZI®) + gemcitabine + cisplatin, followed by cystectomy, then adjuvant durvalumab (IMFINZI®) for cis-eligible MIBC4||
Neoadjuvant durvalumab (IMFINZI®) + gemcitabine + cisplatin, followed by cystectomy, then adjuvant durvalumab (IMFINZI®) for cis-eligible MIBC4||
||See the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for detailed recommendations, including other preferred treatment options.4
NCCN=National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®).
In the treatment of cis-eligible MIBC
OVERALL SURVIVAL (secondary endpoint)1,3
REDUCTION IN RISK OF DEATH with the NIAGARA Regimen† vs neoadjuvant gem-cis (HR=0.75 [95% CI, 0.59-0.93]; P=0.01)
Median OS was not reached with the NIAGARA Regimen† (95% CI, NR-NR) nor with neoadjuvant gem-cis (95% CI, NR-NR)
Median duration of follow-up: 46.3 months (range: 0.03-64.7).
The key secondary endpoint was
OS as assessed with an alpha-allocation approach, following EFS in the
statistical hierarchy.
OVERALL SURVIVAL (secondary endpoint)1,3
OS BY PRESPECIFIED PATIENT SUBGROUP ANALYSIS (exploratory analysis)1,3
|
|
|
|---|
SCROLL
The OS prespecified patient subgroup analysis was not powered to show differences between or within individual subgroups and was not powered for statistical significance.3
*A perioperative regimen consists of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment.1
†The NIAGARA Regimen is defined as neoadjuvant IMFINZI + gem-cis followed by adjuvant IMFINZI as a single agent after RC.1
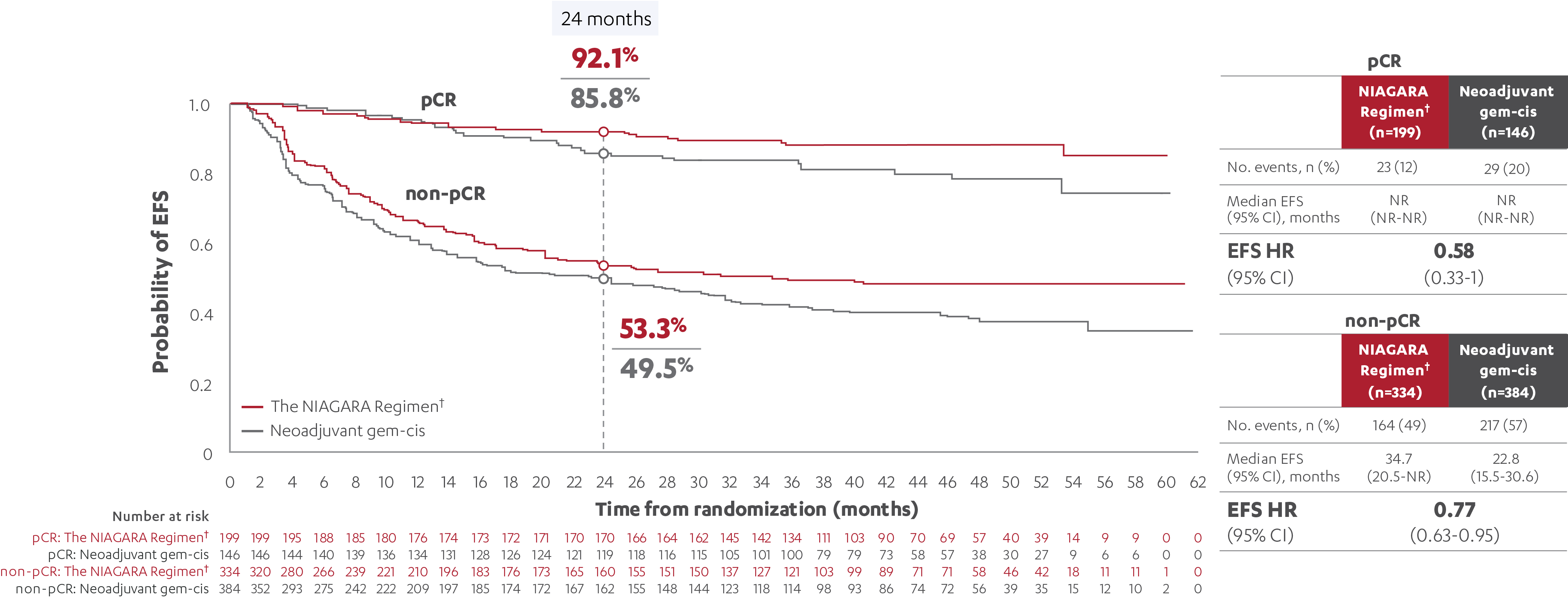
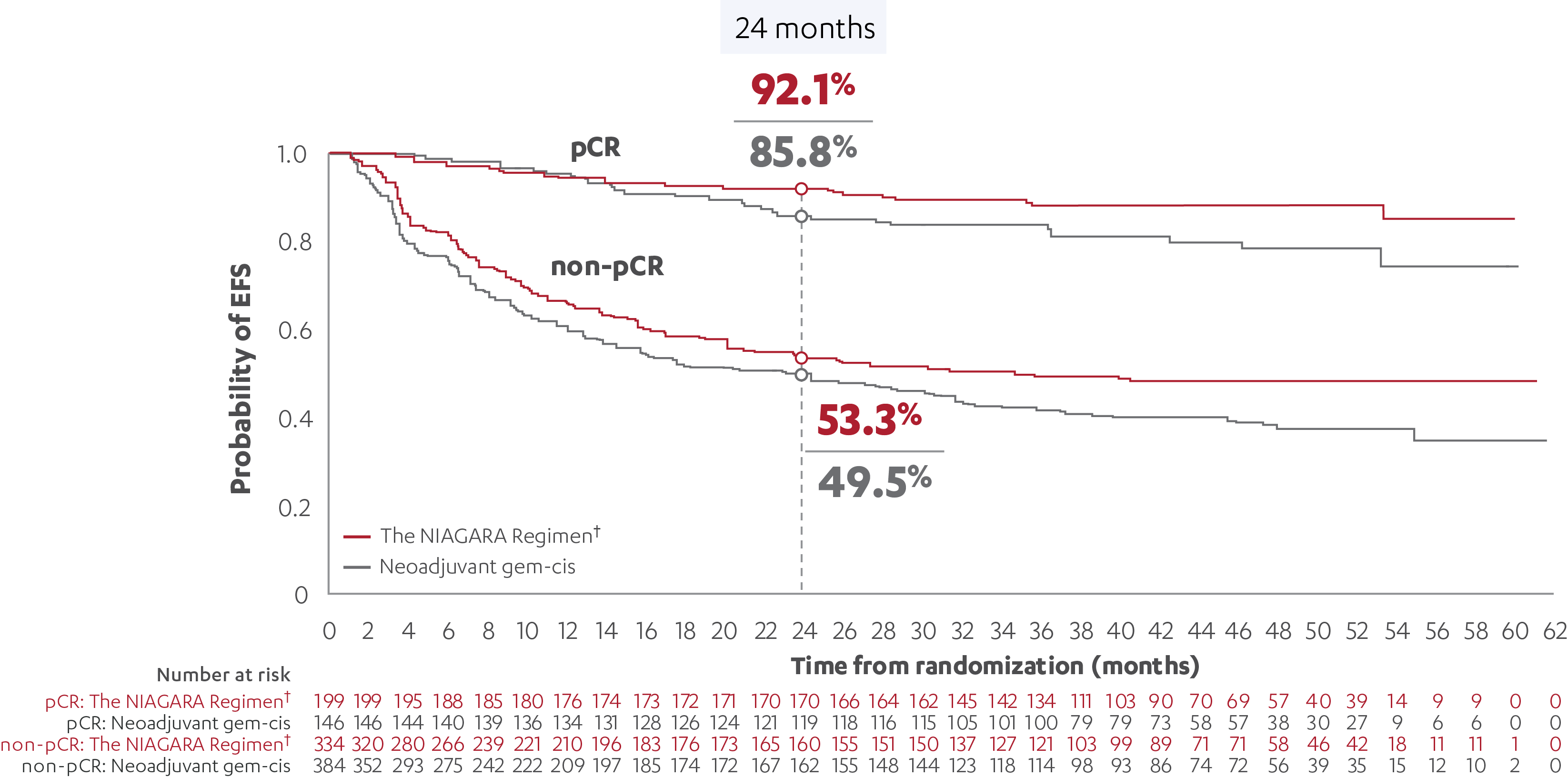
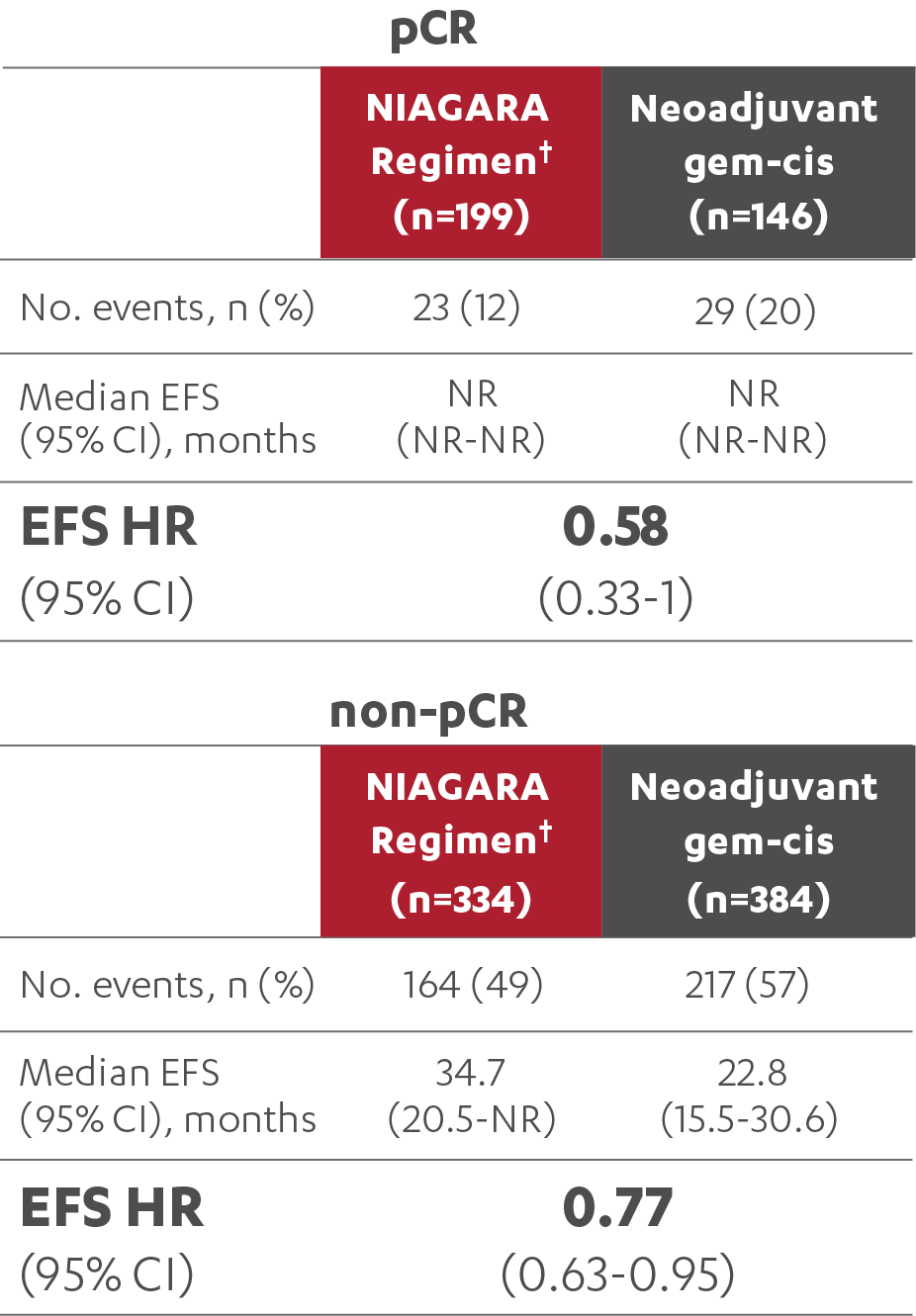
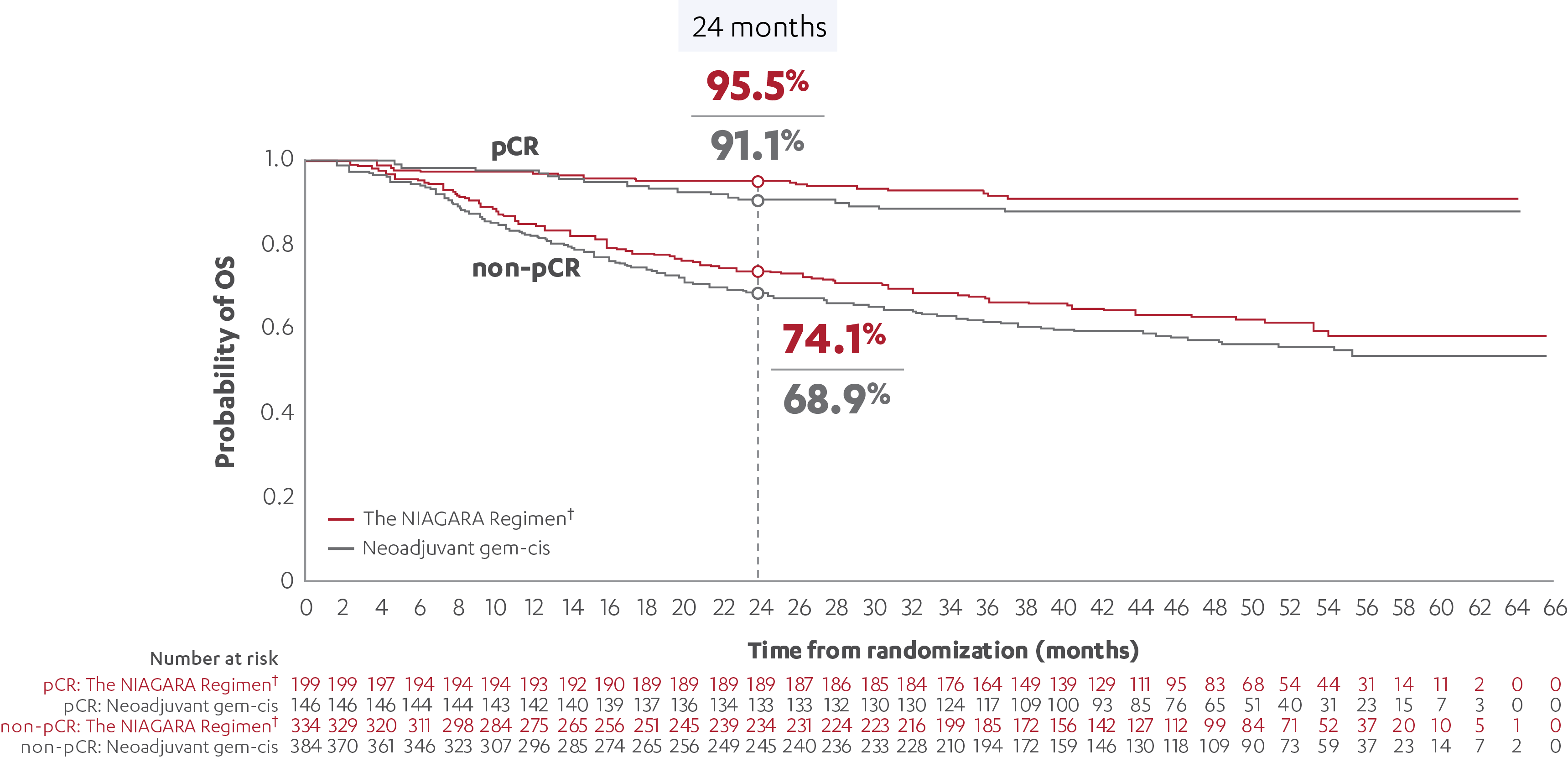
EFS RESULTS IN PATIENTS WITH AND WITHOUT A pCR (post-hoc analysis)5
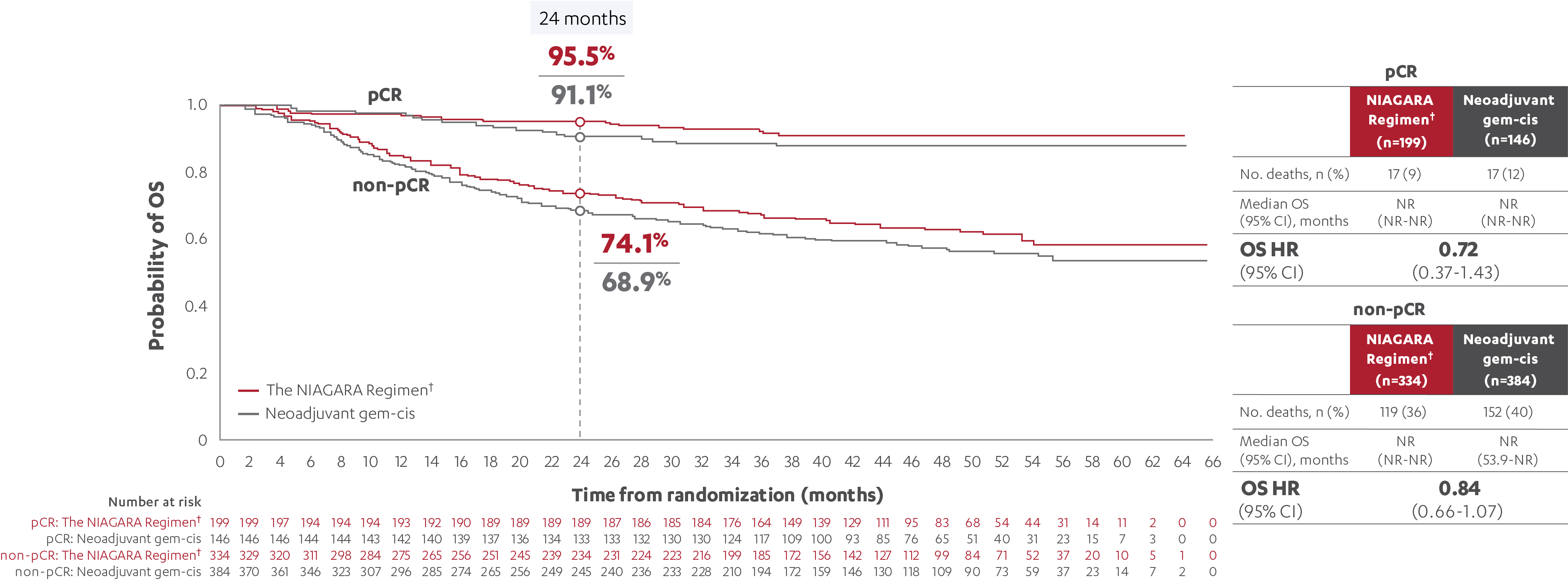
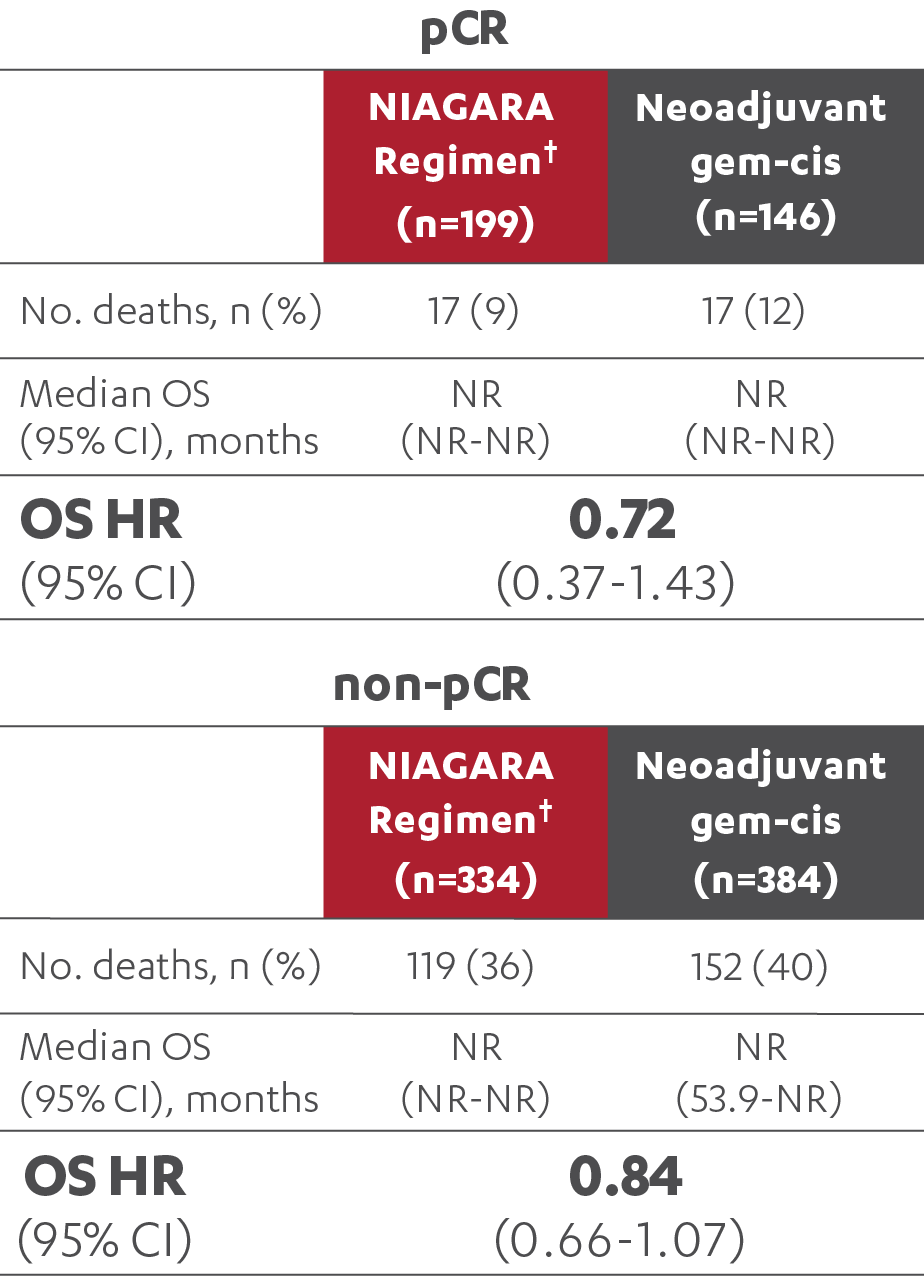
OS RESULTS IN PATIENTS WITH AND WITHOUT A pCR (post-hoc analysis)5
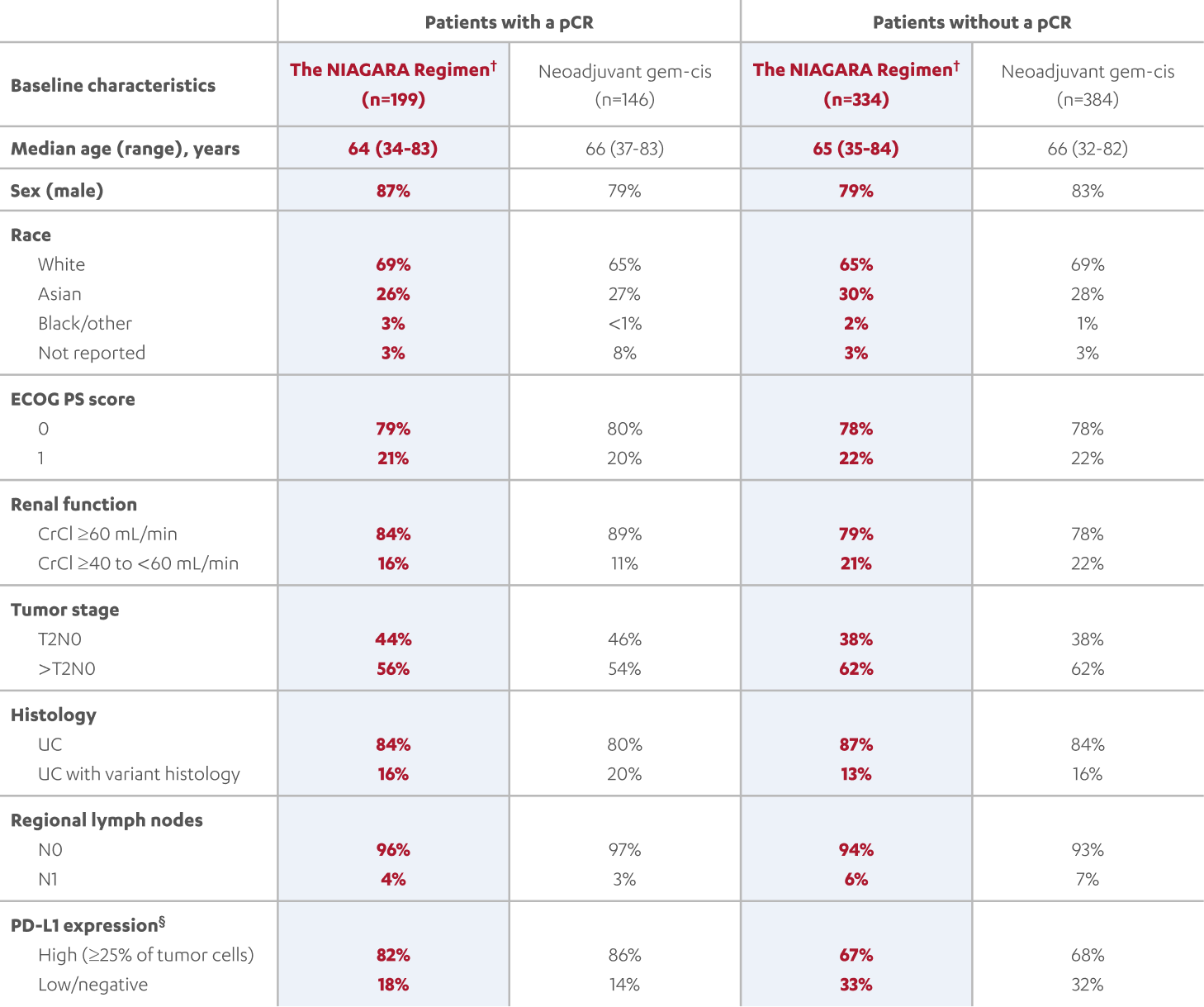
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS IN PATIENTS WITH AND WITHOUT A pCR (post-hoc analysis)1,3,5
|
|
|
|---|
SCROLL
*Event-free survival was defined as the time from randomization to first recurrence of disease post-RC, time to first documented progression in patients who were precluded from RC, time of expected surgery in patients who refused RC or failure to undergo RC due to residual disease, or death due to any cause, whichever occurs first.3
†The NIAGARA Regimen is defined as neoadjuvant IMFINZI + gem-cis followed by adjuvant IMFINZI as a single agent after RC.1
‡At the reanalysis (data cutoff: April 2024), 37.3% (n=199/533; 95% CI, 33.2-41.6) of patients treated with the NIAGARA Regimen† and 27.5% (n=146/530; 95% CI, 23.8-31.6) of patients treated with neoadjuvant gem-cis achieved a pCR.3
§Assessed with the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay using the TC/IC25% algorithm. High PD-L1 expression was defined as ≥25% of TCs with any membrane staining, or ICs staining for PD-L1 at any intensity.5
PERCENTAGE OF PATIENTS WHO UNDERWENT RC1,3
REASONS FOR NOT UNDERGOING OR COMPLETING RC3
| The NIAGARA Regimen* (n=533) |
Neoadjuvant gem-cis (n=530) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients who did not undergo surgery–no. (%) | 63 (11.8%) | 84 (15.8%) | |
| Patient decision | 6% | 6.8% | |
| Unfit for surgery | 0.4% | 1.1% | |
| Adverse event† | 1.1% | 1.3% | |
| Disease progression | 1.7% | 1.7% | |
| Death | 0.9% | 1.5% | |
| Study discontinuation | 0.6% | 2.3% | |
| Investigator decision | 0.9% | 1.1% | |
| Abandoned surgery (intra-operative) | 0.2% | 0% | |
Patient decision was the primary reason for not undergoing RC
SCROLL
The percentage of patients with an adverse reaction‡ that prevented RC was
the same across both treatment arms (0.2%)1
*The NIAGARA Regimen is defined as neoadjuvant IMFINZI + gem-cis followed by adjuvant IMFINZI as a single agent after RC.1
†Adverse event: Any untoward medical occurrence associated with the use of a drug in humans, whether or not considered drug related.6
‡Adverse reaction: Any adverse event caused by a drug. Adverse reactions are a subset of all suspected adverse reactions where there is a reason to conclude that the drug caused the event.6
§Defined as occurring more than 56 days after the last dose of neoadjuvant treatment.1
NIAGARA was the largest Phase III study in cis-eligible MIBC, with >1000 patients1,2
NIAGARA STUDY DESIGN: PHASE III, MULTICENTER, OPEN-LABEL STUDY1,3
Key inclusion criteria
Stratification factors
Key exclusion criteria1:
Dual primary endpoints (ITT)3:
Select secondary endpoints1,3:
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS (ITT)3
| Baseline characteristics | The NIAGARA Regimen¶ (n=533) |
Neoadjuvant gem-cis (n=530) |
|---|---|---|
| Median age (range), years | 65 (34-84) | 66 (32-83) |
| Sex (male) | 82% | 82% |
| Race# White Asian Black/other Missing data |
66% 29% 2% 3% |
68% 27% 1% 4% |
| Region — no. (%) Europe Asia North American and Australia South America |
50% 28% 12% 10% |
54% 27% 12% 7% |
| ECOG PS score** 0 1 |
78% 22% |
78% 22% |
| Current/former smoker | 71% | 75% |
| Histology type†† Urothelial carcinoma Urothelial carcinoma with variant histology |
86% 14% |
83% 17% |
| Tumor stage††‡‡ T2N0 >T2N0 |
40% 60% |
40% 60% |
| Regional lymph nodes†† N0 N1 |
95% 5% |
94% 6% |
| PD-L1 expression§§ High (≥25% of tumor cells) Low/negative |
73% 27% |
73% 27% |
| Renal function Adequate (CrCl ≥60 mL/min) Borderline (CrCl ≥40 to <60 mL/min) |
81% 19% |
81% 19% |
~1 out of 7 patients treated with the NIAGARA Regimen* had UC with variant histology
19% of patients
treated with the NIAGARA Regimen* had borderline renal function (CrCl ≥40 to
<60 mL/min)
27% of patients treated with the NIAGARA Regimen* had PD-L1 low/negative expression
SCROLL
#Race was reported by the patient.
**ECOG PS scores range from 0 to 5, with higher scores indicating greater disability.
††Histologic type, tumor stage, and regional lymph-node stage were assessed by the investigator on the basis of a pathological tumor assessment of a sample obtained during transurethral resection of the bladder tumor, an examination of the patient under anesthesia after the transurethral resection of the bladder tumor, and findings on computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
‡‡Tumor staging was performed according to the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer AJCC Cancer Staging Manual.
§§Baseline samples were assessed with the Ventana PD-L1 (SP263) assay (Ventana Medical Systems) according to the TC/IC25% algorithm, in which a high expression level was defined as PD-L1 expression on at least 25% of tumor cells, at least 25% of immune cells if immune cells were present in more than 1% of the tumor area, or 100% of immune cells if immune cells were present in 1% of the tumor area.
Baseline disease characteristics were well balanced across treatment arms3
*A perioperative regimen consists of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment.1
†Patients with borderline renal function (CrCl ≥ 40mL/min to <60 mL/min) received split-dose cisplatin (35 mg/m2 on Days 1 and 8 of each cycle).1,3
‡Day 1: Cisplatin 70 mg/m2, gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2; Day 8: Gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2; every 21 days for 4 cycles.1,3
§Or by CPR if a biopsy was needed for analysis of a suspected new lesion.3
||Event-free survival was defined as the time from randomization to first recurrence of disease post-RC, time to first documented progression in patients who were precluded from RC, time of expected surgery in patients who refused RC or failure to undergo RC due to residual disease, or death due to any cause, whichever occurs first.3
¶The NIAGARA Regimen is defined as neoadjuvant IMFINZI + gem-cis followed by adjuvant IMFINZI as a single agent after RC.1
There are no contraindications for IMFINZI® (durvalumab) or IMJUDO® (tremelimumab-actl).
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated
Adverse Reactions
Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed under Warnings and Precautions may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. Immune-mediated adverse reactions can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation. Monitor patients closely for symptoms and signs that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate clinical chemistries including liver enzymes, creatinine, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level, and thyroid function at baseline and before each dose. In cases of suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions, initiate
IMFINZI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable Stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
IMFINZI in combination with platinum-containing chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment, followed by IMFINZI continued as a single agent as adjuvant treatment after surgery, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with resectable (tumors ≥4 cm and/or node positive) NSCLC and no known epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements.
IMFINZI, in combination with IMJUDO and platinum-based chemotherapy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC with no sensitizing EGFR mutations or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
IMFINZI, in combination with etoposide and either carboplatin or cisplatin, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
There are no contraindications for IMFINZI® (durvalumab) or IMJUDO® (tremelimumab-actl).
Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed under Warnings and Precautions may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. Immune-mediated adverse reactions can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation. Monitor patients closely for symptoms and signs that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate clinical chemistries including liver enzymes, creatinine, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level, and thyroid function at baseline and before each dose. In cases of suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions, initiate appropriate workup to exclude alternative etiologies, including infection. Institute medical management promptly, including specialty consultation as appropriate. Withhold or permanently discontinue IMFINZI and IMJUDO depending on severity. See USPI Dosing and Administration for specific details. In general, if IMFINZI and IMJUDO requires interruption or discontinuation, administer systemic corticosteroid therapy (1 mg to 2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent) until improvement to Grade 1 or less. Upon improvement to Grade 1 or less, initiate corticosteroid taper and continue to taper over at least 1 month. Consider administration of other systemic immunosuppressants in patients whose immune-mediated adverse reactions are not controlled with corticosteroid therapy.
IMFINZI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable Stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (cCRT).
IMFINZI in combination with platinum-containing chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment, followed by IMFINZI continued as a single agent as adjuvant treatment after surgery, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with resectable (tumors ≥4 cm and/or node positive) NSCLC and no known epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements.
IMFINZI, in combination with IMJUDO and platinum-based chemotherapy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC with no sensitizing EGFR mutations or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
IMFINZI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (cCRT).
IMFINZI, in combination with etoposide and either carboplatin or cisplatin, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
IMFINZI, in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer (BTC).
IMFINZI in combination with IMJUDO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC).
IMFINZI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel followed by IMFINZI as a single agent is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer that is mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test.
IMFINZI in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin as neoadjuvant treatment, followed by single agent IMFINZI as adjuvant treatment following radical cystectomy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC).
IMFINZI in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin and docetaxel (FLOT) as neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment, followed by single agent IMFINZI, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with resectable gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GC/GEJC).
IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause immune-mediated pneumonitis, which may be fatal. The incidence of pneumonitis is higher in patients who have received prior thoracic radiation.
IMFINZI with IMJUDO and platinum-based chemotherapy can cause immune-mediated colitis, which may be
fatal.
IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause immune-mediated colitis that is frequently associated with diarrhea.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation has been reported in patients with corticosteroid-refractory
immune-mediated colitis. In cases of corticosteroid-refractory colitis, consider repeating infectious workup
to exclude alternative etiologies.
IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause immune-mediated hepatitis, which may be fatal.
IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause immune-mediated nephritis.
IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause immune-mediated rash or dermatitis. Exfoliative dermatitis, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), has occurred with PD-1/L-1 and CTLA-4 blocking antibodies. Topical emollients and/or topical corticosteroids may be adequate to treat mild to moderate non-exfoliative rashes.
IMFINZI in combination with IMJUDO can cause immune-mediated pancreatitis. Immune-mediated pancreatitis occurred in 2.3% (9/388) of patients receiving IMFINZI and IMJUDO, including Grade 4 (0.3%) and Grade 3 (1.5%) adverse reactions.
The following clinically significant, immune-mediated adverse reactions occurred at an incidence of less than 1% each in patients who received IMFINZI and IMJUDO or were reported with the use of other immune-checkpoint inhibitors.
IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause severe or life-threatening infusion-related reactions. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions. Interrupt, slow the rate of, or permanently discontinue IMFINZI and IMJUDO based on the severity. See USPI Dosing and Administration for specific details. For Grade 1 or 2 infusion-related reactions, consider using pre-medications with subsequent doses.
Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) before or after being treated with a PD-1/L-1 blocking antibody. Transplant-related complications include hyperacute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), acute GVHD, chronic GVHD, hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) after reduced intensity conditioning, and steroid-requiring febrile syndrome (without an identified infectious cause). These complications may occur despite intervening therapy between PD-1/L-1 blockade and allogeneic HSCT. Follow patients closely for evidence of transplant-related complications and intervene promptly. Consider the benefit versus risks of treatment with a PD-1/L-1 blocking antibody prior to or after an allogeneic HSCT.
Based on their mechanism of action and data from animal studies, IMFINZI and IMJUDO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. In females of reproductive potential, verify pregnancy status prior to initiating IMFINZI and IMJUDO and advise them to use effective contraception during treatment with IMFINZI and IMJUDO and for 3 months after the last dose of IMFINZI and IMJUDO.
There is no information regarding the presence of IMFINZI and IMJUDO in human milk; however, because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from IMFINZI and IMJUDO, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose.
The safety and effectiveness of IMFINZI and IMJUDO have not been established in pediatric patients.
IMFINZI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable Stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (cCRT).
IMFINZI in combination with platinum-containing chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment, followed by IMFINZI continued as a single agent as adjuvant treatment after surgery, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with resectable (tumors ≥4 cm and/or node positive) NSCLC and no known epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements.
IMFINZI, in combination with IMJUDO and platinum-based chemotherapy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC with no sensitizing EGFR mutations or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
IMFINZI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (cCRT).
IMFINZI, in combination with etoposide and either carboplatin or cisplatin, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
IMFINZI, in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer (BTC).
IMFINZI in combination with IMJUDO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC).
IMFINZI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel followed by IMFINZI as a single agent is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer that is mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test.
IMFINZI in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin as neoadjuvant treatment, followed by single agent IMFINZI as adjuvant treatment following radical cystectomy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC).
IMFINZI in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin and docetaxel (FLOT) as neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment, followed by single agent IMFINZI, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with resectable gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GC/GEJC).
Please see Full Prescribing Information including Medication Guide for IMFINZI and IMJUDO.
You may report side effects
related to AstraZeneca products  .
.